来自美国冷泉港实验室沃森生物科学学院,霍德华休斯医学院等处的研究人员建立了一种可获得发夹RNA转基因小鼠模型的快速可扩展系统,从而解决了RNA干扰的转基因小鼠模型可重复性低的问题。这一研究成果公布在Cell杂志上。
领导这一研究的是冷泉港实验室沃森生物科学学院教授Scott W. Lowe,Lowe教授是RNAi小鼠模型研究方面的领先科学家,文章的另外一位作者:冷泉港实验室Gregory J. Hannon教授则是小RNA研究领域的先驱,曾主编了冷泉港实验室技术手册:《MicroRNA研究方法》等。
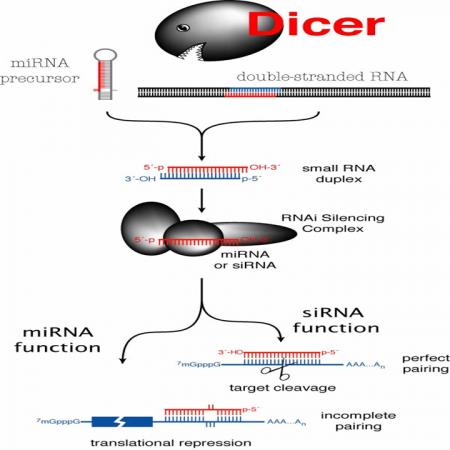
RNAi沉默基因表达示意图
RNA干扰是目前生命科学领域中的前沿技术,从发现至今,科学家们不仅将基因功能研究的希望寄托在这种能阻断基因表达的技术上,而且还都将治愈疑难疾病的希望也付之于其上,但是随着研究的深入,科学家们也发现要在实际操作中进行基因沉默也不是一件容易的事,尤其是在一些实验中,无法实现RNA干扰转基因小鼠的重复形成。
在这篇文章中,研究人员将荧光耦合miR30为基础的shRNAs进行优化,并结合高效胚胎干细胞靶向,建立了一种可获得发夹RNA转基因小鼠模型的快速可扩展系统。研究人员利用这一系统,完成了8种tet-调节的发夹RNA转基因系,包括靶向Firefl和Renilla荧光素酶,Oct4,肿瘤抑制基因p53,p16INK4a, p19ARF,APC,以及已证明为高效敲除的GFP沉默,这些在体内组织中都呈现广泛性敲除。
研究人员还通过靶向APC的shRNAs敲除,发现了这一系统如何识别出预测的表型,以及已充分研究的基因的功能。而且通过基因沉默调控,研究人员还验证了APC/Wnt,和p19ARF作为T细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病/淋巴瘤和肺腺癌潜在治疗靶标的作用。这些实验数据都说明这一系统是一个可获得任何哺乳动物基因RNAi转基因小鼠得到低成本,可扩展平台。
Lowe教授和Hannon教授在此之前还发表了一篇RNAi技术的重要文章:他们发现了一种能帮助研究人员一次筛选上千候选发夹RNA分子,从中找到能沉默目标基因的RNA分子的新方法(具体内容请见:RNAi技术先驱:一种提高沉默效率新方法 )。
原文摘要:
A Rapid and Scalable System for Studying Gene Function in Mice Using Conditional RNA Interference
Highlights
shRNA transgenics enable potent and reversible fluorescence-marked gene silencing
Transgenic mouse production is fast, efficient, and scalable
Speedy ES cells accelerate the evaluation of gene function in mouse models
Reversible gene suppression can pinpoint pathways for therapeutic intervention
Summary
RNA interference is a powerful tool for studying gene function, however, the reproducible generation of RNAi transgenic mice remains a significant limitation. By combining optimized fluorescence-coupled miR30-based shRNAs with high efficiency ES cell targeting, we developed a fast, scalable pipeline for the production of shRNA transgenic mice. Using this system, we generated eight tet-regulated shRNA transgenic lines targeting Firefly and Renilla luciferases, Oct4 and tumor suppressors p53, p16INK4a, p19ARF and APC and demonstrate potent gene silencing and GFP-tracked knockdown in a broad range of tissues in vivo. Further, using an shRNA targeting APC, we illustrate how this approach can identify predicted phenotypes and also unknown functions for a well-studied gene. In addition, through regulated gene silencing we validate APC/Wnt and p19ARF as potential therapeutic targets in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma and lung adenocarcinoma, respectively. This system provides a cost-effective and scalable platform for the production of RNAi transgenic mice targeting any mammalian gene.