科幻电影《神奇旅程》中,一个微型的潜水艇被注射进一个快要死去的人体血管,目的是清除让病人有生命危险的血栓。一个新的探针非常类似这个虚构的微潜水艇的尾部:它能够穿过动脉定位出最危险的血块和积垢。
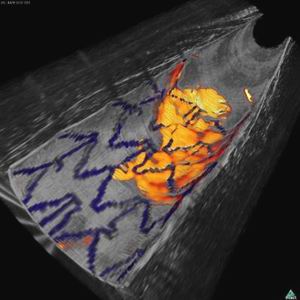
结合光学成像和近红外荧光图像显示兔子动脉内表面,蓝色为植入的支架,红黄色为纤维蛋白沉积
现有的探针本质上来说是能够在动脉里穿行的照相机,医生必须认出堆积物,并判断它们是否有可能变松并堵塞动脉。美国波士顿马萨诸塞州医院Guillermo Tearney发明的一种新型探针,能够检测分子并标记到最危险的血块和脂肪斑。
为了检验这款探针,Tearney的团队先是喂食了产生动脉积垢的兔子,并用荧光对危险信号分子进行标记。探针的探测器带有荧光进入了动脉,在动脉壁上显示亮区标记他们发现的目标。
这个小组能够检测到一种引发血块形成的纤维蛋白,和组织蛋白酶B的形成,在最危险的斑块中有发现这样的酶。
Tearney说原则上来说任何分子都可以被检测到,包括癌症的分子标记物。虽然这需要更一步的发展,但结合探针对抗危险的斑块还是有可能的。
检测纤维蛋白对于那些患有动脉阻塞并通过支架手术进行疏通的患者非常重要,因为手术后血管很快会再次阻塞,而再次阻塞的第一迹象就是支架上的纤维蛋白沉积。
目前的探针无法区分正常的纤维蛋白沉淀,比如支架上的那些细胞。但荧光检测可以,所以医生可以在血栓形成前给患者开溶解血块的药物。
Tearney现在打算对冠状动脉疾病的患者进行该装置测试。(生物探索译)
相关英文论文摘要:
Intra-arterial catheter for simultaneous microstructural and molecular imaging in vivo
Advancing understanding of human coronary artery disease requires new methods that can be used in patients for studying atherosclerotic plaque microstructure in relation to the molecular mechanisms that underlie its initiation, progression and clinical complications, including myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death. Here we report a dual-modality intra-arterial catheter for simultaneous microstructural and molecular imaging in vivo using a combination of optical frequency domain imaging (OFDI) and near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) imaging. By providing simultaneous molecular information in the context of the surrounding tissue microstructure, this new catheter could provide new opportunities for investigating coronary atherosclerosis and stent healing and for identifying high-risk biological and structural coronary arterial plaques in vivo.
英文论文链接:https://www.nature.com/nm/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nm.2555.html







