microRNA是近年来发现的一种单链的短链RNA,长度约22个碱基,在动植物及人类中广泛存在,与发育、分化、凋亡、脂肪代谢、病毒感染和癌症等多种重要生物学过程有密切的联系,并显示出作为癌症、心血管等重大疾病等方面的新的分子标记物的巨大潜力,是近十年来的一个研究的热点。对microRNA表达谱进行高通量、低成本的检测对于该领域的发展具有重要的意义。
中科院苏州纳米技术与纳米仿生研究所李炯课题组与生物物理所阎锡蕴课题组合作,首次实现了高通量microRNA芯片的非标记检测,而其他芯片和测序技术需要数小时的手工操作才能完成标记,从而大幅度降低了检测的标记时间和成本。
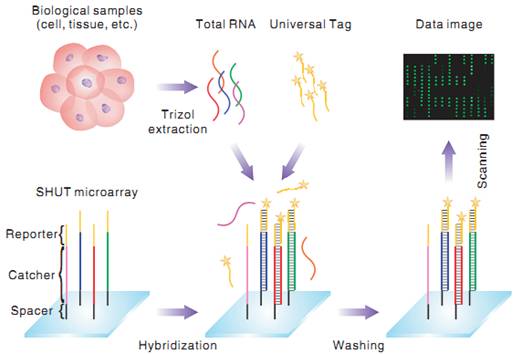
图1. 高通量microRNA非标记检测原理示意图
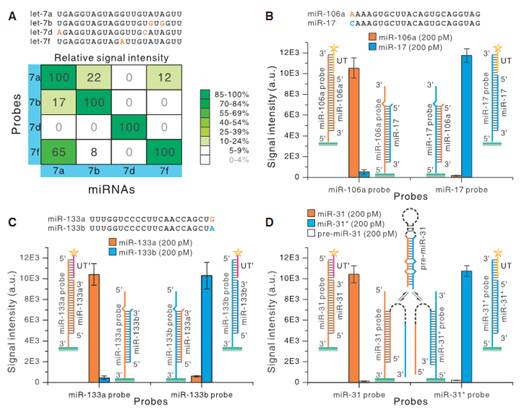
图2. 选择性
与其他商业化microRNA芯片技术相比,该技术还具有如下独特的优势:1. 高灵敏度,由于减少了标记带来的损失,仅用100ng的总RNA就可以得到较好的结果;2. 完美识别前体microRNA,解决了芯片技术在这方面的缺陷,因此无需纯化小RNA,可以直接使用总RNA,减少了实验的操作步骤;3. 可以对microRNA链中的中间或者是两端的单碱基错配都能有效识别,这也是其他芯片技术无法实现的;4. 可应用于植物microRNA表达谱检测。植物microRNA在3'端普遍存在甲基化的问题,对于主流的酶标记方法来说效率很低(~10%),因此多数芯片技术无法直接应用于植物microRNA表达谱的检测,测序技术在文库构建的时候也会受到类似的影响,少数公司则采用了非主流的化学标记的方法。而该技术基于核酸杂交,完全不受甲基化的影响。另外,该技术无需特殊设备,常规的芯片制作和扫描设备就可以应用,从而最大程度地减少了进入市场的难度。
即使与现在发展迅猛的测序技术相比,该技术对于microRNA表达谱检测在通量(大量样品)、成本、灵敏度以及后续的数据分析等方面仍然具有明显的优势。该工作近期发表于Nucleic Acid Research杂志上。
目前,研究人员正努力标准化该技术,为其尽早进入市场铺平道路。
此项工作得到中科院和国家自然科学基金委的大力支持。
相关英文论文摘要:
Label-free high-throughput microRNA expression profiling from total RNA
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key biological regulators and promising disease markers whose detection technologies hold great potentials in advancing fundamental research and medical diagnostics. Currently, miRNAs in biological samples have to be labeled before being applied to most high-throughput assays. Although effective, these labeling-based approaches are usually labor-intensive, time-consuming and liable to bias. Besides, the cross-hybridization of co-existing miRNA precursors (pre-miRNAs) is not adequately addressed in most assays that use total RNA as input. Here, we present a hybridization-triggered fluorescence strategy for label-free, microarray-based high-throughput miRNA expression profiling. The total RNA is directly applied to the microarray with a short fluorophore-linked oligonucleotide Universal Tag which can be selectively captured by the target-bound probes via base-stacking effects. This Stacking-Hybridized Universal Tag (SHUT) assay has been successfully used to analyze as little as 100 ng total RNA from human tissues, and found to be highly specific to homogenous miRNAs. Superb discrimination toward single-base mismatch at the 5′ or 3′ end has been demonstrated. Importantly, the pre-miRNAs generated negligible signals, validating the direct use of total RNA.
英文论文链接:https://www.biodiscover.com/news/biotechnology/library/1414







