中国科学院上海生命科学研究院营养研究所刘勇研究组,新近揭示了肝脏中内质网应激介导血糖调节发生紊乱的新机制,其论文近日在线发表在《美国科学院院刊》上。专家认为,该研究提示,特异调节肝脏内质网跨膜蛋白IRE1α的活性具有防治2型糖尿病的潜力。
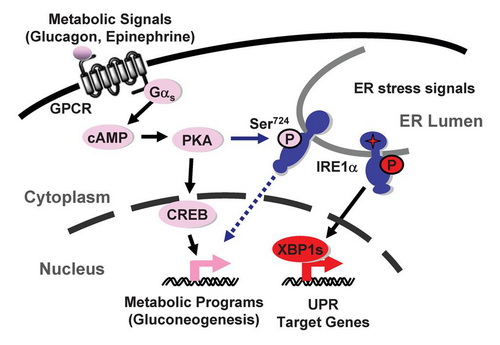
内质网应激IRE1通路参与肝脏血糖调节的信号机制
据介绍,在营养失衡导致肥胖与2型糖尿病等代谢疾病的发生、发展中,细胞应激扮演着重要角色。肝脏中内质网作为真核细胞中蛋白质折叠加工与质量监控、脂类合成与分泌的重要细胞器,其稳态平衡对于维持细胞功能至关重要。
当内质网不能承担蛋白折叠的高负荷或内质网中脂类代谢发生异常,就会引发细胞内质网应激而激活未折叠蛋白响应,从而增强内质网的应对处理能力。大量研究显示,内质网应激是连接肥胖、胰岛素抵抗和2型糖尿病的重要病理机制之一。
内质网跨膜蛋白IRE1α是一种内质网应激感应分子,可以通过自身磷酸化被激活,在细胞应激状况下参与决定细胞的生死命运。
刘勇研究组博士研究生毛婷、邵孟乐等通过动物模型研究发现,肝脏中IRE1α信号通路可以感应机体能量变化,在禁食情况下IRE1α被磷酸化激活。进一步研究显示,以此活化的IRE1α参与胰高血糖素对肝脏多种代谢途径的调节。在伴有空腹高血糖症状的肥胖小鼠模型中,胰高血糖素水平的异常升高通过蛋白激酶A 作用,使IRE1α处于代谢应激下的过度激活状态,而抑制IRE1α通路则显著改善血糖水平并提高机体的葡萄糖耐受能力。
相关英文论文摘要:
PKA phosphorylation couples hepatic inositol-requiring enzyme 1α to glucagon signaling in glucose metabolism
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident protein kinase/endoribonuclease inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) is activated through transautophosphorylation in response to protein folding overload in the ER lumen and maintains ER homeostasis by triggering a key branch of the unfolded protein response. Here we show that mammalian IRE1α in liver cells is also phosphorylated by a kinase other than itself in response to metabolic stimuli. Glucagon-stimulated protein kinase PKA, which in turn phosphorylated IRE1α at Ser724, a highly conserved site within the kinase activation domain. Blocking Ser724 phosphorylation impaired the ability of IRE1α to augment the up-regulation by glucagon signaling of the expression of gluconeogenic genes. Moreover, hepatic IRE1α was highly phosphorylated at Ser724 by PKA in mice with obesity, and silencing hepatic IRE1α markedly reduced hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance. Hence, these results suggest that IRE1α integrates signals from both the ER lumen and the cytoplasm in the liver and is coupled to the glucagon signaling in the regulation of glucose metabolism.







