据每日科学网9月26日报道,瑞典卡罗琳斯卡医学院的科学家们揭示了脂肪细胞功能障碍与肥胖症、糖尿病和血脂紊乱疾病之间的关系。
该研究的论文发表在最新一期的《Nature》杂志上,研究结果显示肥胖病人的脂肪细胞有着较强的脂肪存储功能,但缺乏消耗代谢它们的能力。
论文的第一作者Peter Arner说道:“这是由我们首次证实了健康人群和肥胖症患者的脂肪细胞在代谢功能上存在差异。这为后续开发针对脂肪细胞代谢的治疗方法开辟了一个全新的研究领域。”
科学家采集了大约100个人的组织样品,其中包括有身材苗条的人群和肥胖症患者等。通过检测脂肪细胞中脂肪的存储时间以确定它们代谢的效率和能力。在该研究中,测定脂肪存储时间使用的方法基于放射性同位素碳-14法。
研究结果发现,在健康的人群中,脂肪细胞中存储的脂肪平均每10年要完全更新6次,而在早期II型糖尿病患者的体内,脂肪细胞代谢功能存在障碍,其中存储的脂肪难以被消耗掉。
在高脂血症(一种先天性的血脂代谢紊乱,可引发冠心病)病人中也存在类似情况,它们的脂肪细胞在脂肪存储功能上存在障碍,这就意味着他们血液中的甘油三酸酯和胆固醇浓度会较高。(生物探索 Jun)
生物探索推荐英文论文摘要:
Dynamics of human adipose lipid turnover in health and metabolic disease
Adipose tissue mass is determined by the storage and removal of triglycerides in adipocytes1. Little is known, however, about adipose lipid turnover in humans in health and pathology. To study this in vivo, here we determined lipid age by measuring 14C derived from above ground nuclear bomb tests in adipocyte lipids. We report that during the average ten-year lifespan of human adipocytes, triglycerides are renewed six times. Lipid age is independent of adipocyte size, is very stable across a wide range of adult ages and does not differ between genders. Adipocyte lipid turnover, however, is strongly related to conditions with disturbed lipid metabolism. In obesity, triglyceride removal rate (lipolysis followed by oxidation) is decreased and the amount of triglycerides stored each year is increased. In contrast, both lipid removal and storage rates are decreased in non-obese patients diagnosed with the most common hereditary form of dyslipidaemia, familial combined hyperlipidaemia. Lipid removal rate is positively correlated with the capacity of adipocytes to break down triglycerides, as assessed through lipolysis, and is inversely related to insulin resistance. Our data support a mechanism in which adipocyte lipid storage and removal have different roles in health and pathology. High storage but low triglyceride removal promotes fat tissue accumulation and obesity. Reduction of both triglyceride storage and removal decreases lipid shunting through adipose tissue and thus promotes dyslipidaemia. We identify adipocyte lipid turnover as a novel target for prevention and treatment of metabolic disease.
Figures at a glance:
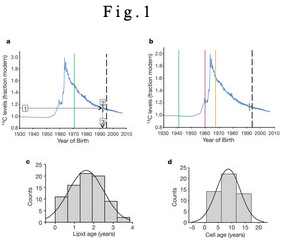
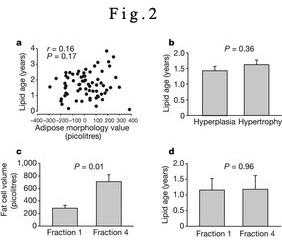
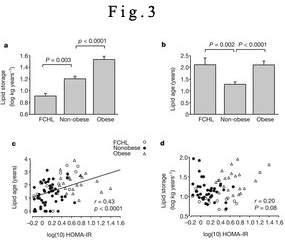
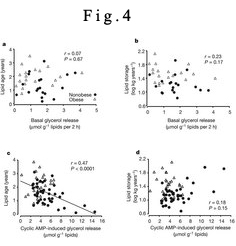
Figure 1: Atmospheric 14C over time and its use to determine lipid age and adipocyte age.
Figure 2: Relationship between adipocyte size and lipid age.
Figure 3: Lipid turnover in subcutaneous fat.
Figure 4: Correlation between lipid turnover and adipocyte lipolysis.







