摘要:20多年来,与肥胖相关的疾病在西方国家日益流行。据美国物理学家组织网7月27日(北京时间)报道,近日,美国阿尔伯特·爱因斯坦医学院研究人员通过研究营养过剩与肥胖之间的生理机制发现,大脑对体内葡萄糖动态变化的感知缺陷会导致肥胖和相关疾病。他们还同时找到了矫正这种缺陷的方法,能使整个身体能量达到平衡,以治疗肥胖症。研究论文发表在7月26日出版的《公共科学图书馆—生物学》(PLoS Biology)上。
下丘脑在控制能量与身体重量平衡方面扮演重要角色。为了在能量摄入和能量消耗之间保持平衡,下丘脑要不断检测一些激素(如胰岛素和瘦蛋白)和营养成分(如葡萄糖)的循环,以了解整个身体的能量水平。领导该研究的爱因斯坦医学院神经内分泌学与新陈代谢专家蔡东升(音译)介绍说,尽管我们已经掌握了许多下丘脑调控摄食的激素路径,但下丘脑对营养成分的感知机制、营养感知缺陷和肥胖症之间的关系还不明确。
研究人员通过小鼠实验发现,一种名为缺氧诱导因子的蛋白质复合物,在下丘脑葡萄糖感知功能和整体能量平衡中发挥重要作用。缺氧诱导因子是引起缺氧反应的核心转录因子,当机体组织中含氧水平低时,缺氧诱导因子会被激活,促进细胞改变代谢方式。最近还有研究认为,缺氧诱导因子也参与了肿瘤细胞的代谢。“但缺氧诱导因子在整个机体新陈代谢调控中的重要性此前未曾深入研究,”蔡东升说。
研究人员还发现,缺氧诱导因子能被葡萄糖激活,这表明它和食欲控制相关。缺氧诱导因子在下丘脑营养感知神经元中引发了POMC基因(下丘脑控制摄食和体重的一种关键基因)表达,从而产生了对葡萄糖的反应。
研究人员通过小鼠实验证明,通过基因传递增强下丘脑缺氧诱导因子的活性后,尽管小鼠处于营养过剩状态,仍然能抵抗肥胖。
“我们首次证明了,下丘脑神经元中的缺氧诱导因子还能感知葡萄糖的动态变化水平,从而控制整个机体的能量摄入与支出平衡,这对平衡体重非常关键,”蔡东升说。
生物探索推荐英文论文摘要:
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Directs POMC Gene to Mediate Hypothalamic Glucose Sensing and Energy Balance Regulation
Abstract:
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) is a nuclear transcription factor that responds to environmental and pathological hypoxia to induce metabolic adaptation, vascular growth, and cell survival. Here we found that HIF subunits and HIF2α in particular were normally expressed in the mediobasal hypothalamus of mice. Hypothalamic HIF was up-regulated by glucose to mediate the feeding control of hypothalamic glucose sensing. Two underlying molecular pathways were identified, including suppression of PHDs by glucose metabolites to prevent HIF2α degradation and the recruitment of AMPK and mTOR/S6K to regulate HIF2α protein synthesis. HIF activation was found to directly control the transcription of POMC gene. Genetic approach was then employed to develop conditional knockout mice with HIF inhibition in POMC neurons, revealing that HIF loss-of-function in POMC neurons impaired hypothalamic glucose sensing and caused energy imbalance to promote obesity development. The metabolic effects of HIF in hypothalamic POMC neurons were independent of leptin signaling or pituitary ACTH pathway. Hypothalamic gene delivery of HIF counteracted overeating and obesity under conditions of nutritional excess. In conclusion, HIF controls hypothalamic POMC gene to direct the central nutrient sensing in regulation of energy and body weight balance.
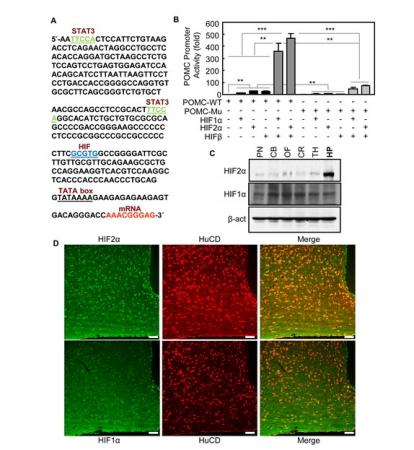
Figure 1. Regulation of HIF on POMC gene and HIF profile in the hypothalamus.







