6月29日,《神经科学杂志》(The Journal of Neuroscience)发表了中科院生物物理研究所脑与认知国家重点实验室袁增强研究组有关c-Abl-MST1信号通路介导的氧化压力条件下的神经细胞凋亡的最新研究成果。该项工作由博士研究生肖磊等在袁增强研究员的指导下完成。
氧化压力影响细胞的生存和稳态,参与了包括神经退行性疾病的病理过程等在内的各种生物学进程,而氧化压力是如何影响这些生命进程的分子机制仍有待阐明。袁增强研究员在哈佛大学的一系列研究工作已经阐明,蛋白激酶MST1通过直接激活转录因子FOXO介导了氧化压力条件下神经细胞的凋亡,然而MST1的上游调控机制尚不清楚。
以此为出发点,肖磊等发现了在氧化压力条件下,酪氨酸激酶c-Abl作为上游激酶,可以引起MST1在酪氨酸433位点的磷酸化 (如图),而这一磷酸化稳定并激活了MST1。一方面,泛素连接酶CHIP介导了MST1泛素化降解过程,c-Abl通过磷酸化MST1抑制了其泛素化降解途径从而稳定了MST1;另一方面,氧化压力引起的MST1酪氨酸433位点的磷酸化加强了MST1与FOXO3之间的相互作用进而激活FOXO3的促凋亡转录功能。
进一步的研究表明,c-Abl介导的MST1酪氨酸433位点的磷酸化对于氧化压力引起的体外原代培养和在体的海马神经元的细胞凋亡至关重要。该研究阐明了c-Abl-MST1信号通路可能参与了神经退行性疾病的病理过程,对于治疗以神经细胞凋亡为特征的老年痴呆症和帕金森氏病等神经退行性疾病提供了理论基础和潜在的药物设计靶标,具有一定的应用前景。
该工作得到了国家自然科学基金,科技部等项目的支持。
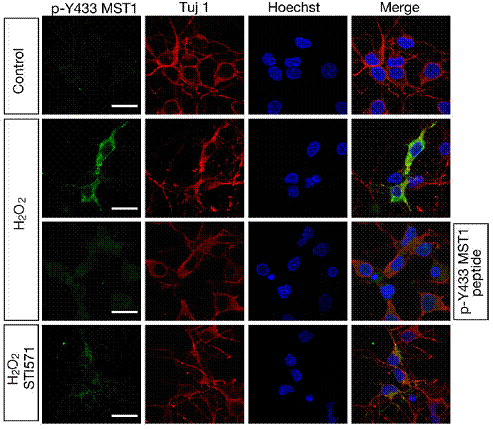
酪氨酸激酶c-Abl作为上游激酶,可以引起MST1在酪氨酸433位点的磷酸化
生物探索推荐英文论文摘要:
The c-Abl-MST1 Signaling Pathway Mediates Oxidative Stress-Induced Neuronal Cell Death
Abstract:
Oxidative stress influences cell survival and homeostasis, but the mechanisms underlying the biological effects of oxidative stress remain to be elucidated. The protein kinase MST1 (mammalian Ste20-like kinase 1) plays a major role in oxidative stress-induced cell death in primary mammalian neurons. However, the mechanisms that regulate MST1 in oxidative stress responses remain largely unknown. In the present study, we demonstrate that the protein kinase c-Abl phosphorylates MST1 at Y433, which triggers the stabilization and activation of MST1. Inhibition of c-Abl promotes the degradation of MST1 through C terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein (CHIP)-mediated ubiquitination, and thereby attenuates cell death. Oxidative stress induces the c-Abl-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of MST1 and increases the interaction between MST1 and FOXO3 (Forkhead box O3), thereby activating the MST1-FOXO signaling pathway, leading to cell death in both primary culture neurons and rat hippocampal neurons. The identification of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase as a novel upstream activator of MST1 suggests that the c-Abl-MST1 signaling cascade plays an important role in cellular responses to oxidative stress.







