摘要:日前研究人员发现人体中普遍存在基因突变,平均每人存在着60种基因突变,这一结果远超出之前的预计。
据英国每日邮报报道,或许这仅是科幻情节捕风捉影式的空想,但日前研究人员发现人体中普遍存在基因突变,也就是说我们普遍具有《X战警》中特异功能人群的潜质。平均每人存在着60种基因突变,这一结果远超出之前的预计。

虽然科学家所发现的基因突变现象并不具有《X战警》中“金刚狼”的利爪,但这项研究结果却是令人惊奇的。
这项最新研究结果是由英国剑桥市韦尔康姆信托桑格协会、美国和加拿大的两家研究机构发现的,他们声称人体内从双亲遗传可获得至多60种基因突变,表明人类基因突变出现在精子和卵子中,而双亲或许并不存在这方面的基因变化。
这项研究也推翻了多数基因突变来自父亲或者母亲的早期理论,研究结果表明基因突变现象戏剧性地出现在每一个体上。为了试着探知人体内有多少“变异基因”,科学家研究了双亲的基因特征,其中包含只有一个孩子的双亲家庭。
研究人员在儿童体内寻找新的基因突变,对每个基因序列进行梳理分析,发现了6000个可能存在的突变现象。他们还研究分析了双亲精子和卵细胞中存在的基因突变,以及婴儿出生之后出现的基因突变现象。这项最新研究现发表在《自然基因学》期刊上,引起了科学家们的高度关注。

《X战警》中“金刚狼”的利爪
研究结果显示,一个家庭中孩子92%的基因变异来自父亲,而来自母亲的基因变异仅有36%。韦尔康姆信托桑格协会的马特-胡勒斯(Matt Hurles)博士是该项研究合著作者之一,他指出,现在我们知道一些家庭的孩子基因突异可能主要来自母亲,其它家庭可能主要来自父亲。
加拿大蒙特利尔大学菲利普-阿瓦达拉(Philip Awadalla)教授也是该项研究合著作者之一,他强调称,目前我们可以通过实验技术中的新进展和新型分析法则测试之前的理论,从而使我们发现一些新的基因突变,这就像从一个大干草堆中寻找小针头。
目前,该研究小组计划展开更深入的研究,试图揭晓像双亲的年龄和生活环境是否会影响下一代的基因突变,以及如何使用这些研究发现来分辨令人体衰弱的基因疾病。
生物探索推荐英文原文:
Variation in genome-wide mutation rates within and between human families
Abstract:
J.B.S. Haldane proposed in 1947 that the male germline may be more mutagenic than the female germline1. Diverse studies have supported Haldane's contention of a higher average mutation rate in the male germline in a variety of mammals, including humans2, 3. Here we present, to our knowledge, the first direct comparative analysis of male and female germline mutation rates from the complete genome sequences of two parent-offspring trios. Through extensive validation, we identified 49 and 35 germline de novo mutations (DNMs) in two trio offspring, as well as 1,586 non-germline DNMs arising either somatically or in the cell lines from which the DNA was derived. Most strikingly, in one family, we observed that 92% of germline DNMs were from the paternal germline, whereas, in contrast, in the other family, 64% of DNMs were from the maternal germline. These observations suggest considerable variation in mutation rates within and between families.
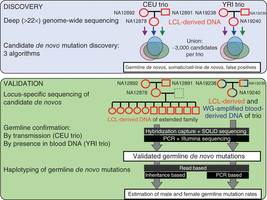
Pictured: The two phases of the project, discovery and validation, are shown schematically, including the samples from each family that were used in each phase. LCL, lymphoblastoid cell line; WG, whole genome.
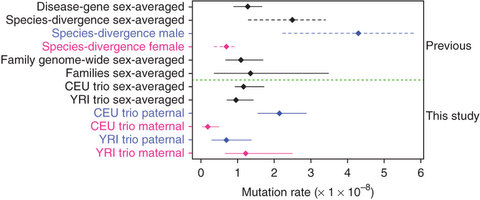
Pictured: Mutation rates estimated from previous studies are shown above the dashed green line. Solid lines encompassing point estimates represent 95% confidence intervals. Dashed lines encompassing point estimates represent reported plausible ranges.







