近日,国际学术期刊Developmental Cell发表了生化与细胞所陈正军研究组有关细胞极性蛋白参与细胞迁移过程的最新研究成果。这项研究发现,重要的细胞紧密联接蛋白,又称封闭蛋白(Occludin),在上皮细胞的定向迁移过程中定位于迁移的上皮细胞的迁移前缘,可能参与细胞定向迁移的极性的形成和稳定,由此调控细胞定向迁移活动。
细胞迁移是一种非常重要的细胞活动现象,它在生物体发育过程以及机体稳态维持方面起着非常重要的作用,也和许多疾病的发生发展紧密相关。细胞迁移过程及其分子调控网络非常复杂,迄今为止,迁移细胞的极性如何形成,极性蛋白如何被招募到上皮细胞迁移前缘等机制,以及极性蛋白的下游信号传导通路仍很不清楚。
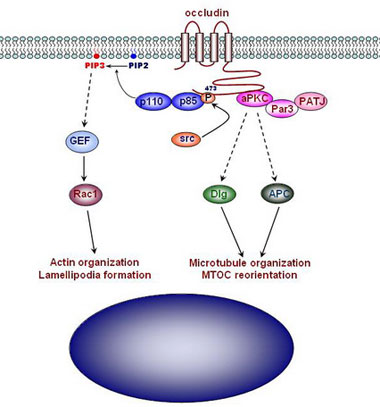
陈正军研究组杜丹博士通过细胞生物学和原子粒显微镜等一系列技术和方法发现了四次跨膜封闭蛋白Occludin定位并富集于迁移的上皮细胞前缘,Occludin表达被干扰后,明显影响其在细胞迁移前缘的定位,并造成细胞微管组织结构紊乱,同时微管组织中心(MTOC)重定向也明显异常;分子机制的研究结果证明Occludin能与aPKC和PI3K结合,且激活aPKC和PI3K信号通路,借此,可能参与调控了微管组织中心定位、细胞骨架组织和细胞伪足突触伸展等过程。这些研究发现提高了人们对迁移细胞极性的形成和稳定,以及细胞生命活动―细胞极性和细胞迁移―内在生物学相关性的认识,同时也为了解胚胎发育过程和愈伤过程增添了新的内容。
生物谷推荐原始出处:
Developmental Cell, Volume 18, Issue 1, 52-63, 19 January 2010 DOI:10.1016/j.devcel.2009.12.008
The Tight Junction Protein, Occludin, Regulates the Directional Migration of Epithelial Cells
Dan Du, Feilai Xu, Lihou Yu, Chenyi Zhang, Xuefeng Lu, Haixin Yuan, Qin Huang, Fan Zhang, Hongyan Bao, Lianghui Jia, Xunwei Wu, Xueliang Zhu, Xiaohui Zhang, Zhe Zhang, Zhengjun Chen
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China Key Laboratory of Molecular Cell Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China Cutaneous Biology Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Charlestown, MA 02129, USA Corresponding author
Cell polarity proteins regulate tight junction formation and directional migration in epithelial cells. To date, the mechanism by which these polarity proteins assemble at the leading edge of migrating epithelial cells remains unclear. We report that occludin, a transmembrane protein, is localized at the leading edge of migrating cells and regulates directional cell migration. During migration, occludin knockdown disrupted accumulation of aPKC-Par3 and PATJ at the leading edge, and led to a disorganized microtubule network and defective reorientation of the microtubule organization center (MTOC). Phosphorylation of occludin at tyrosine 473 residue allowed recruitment of p85α to the leading edge via association with its C-terminal SH2 domain. Loss of occludin attenuated activation of PI3K, leading to disorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and reduced cell protrusions. Our data indicate that occludin is required for the leading-edge localization of polarity proteins aPKC-Par3 and PATJ and promotes cell protrusion by regulating membrane-localized activation of PI3K.







