导读:一项最新研究首次在活体动物实验中提供直接证据,证明大麻素作用于神经胶质细胞上的CB1R,由胶质细胞再来调节神经元突触传递活动,进而引起工作记忆的损伤——配角变成了主角。该研究由陕西师范大学张遐设计和主导,其成果将为牢固确立神经胶质细胞调控学习记忆等大脑高级功能的理论认识作出贡献。
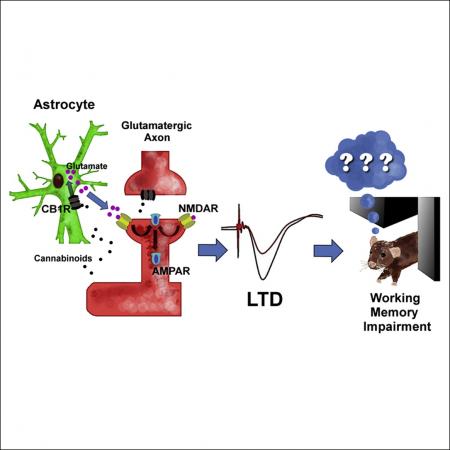
工作记忆是复杂认知活动的基础,而海马CA3-CA1突触即神经细胞之间的连接,其增强和抑制,包括长时程增强(LTP)和长时程抑制(LTD),是学习和记忆形成的关键机制。
张遐团队选择了大麻素对脑功能的影响作为研究路径。他们发现,大麻素首先作用于神经胶质细胞上的大麻素受体(CB1R),激活胶质细胞的活动使海马CA3-CA1兴奋性突触发生LTD,进而导致工作记忆的损伤。
而此前学术界一直认为,占人脑细胞数量10%的神经元是处理高级功能的主体脑细胞,而占90%的胶质细胞仅是对神经元起支持、营养、保护等作用的配角。
“人脑里面也产生自己的大麻素,这就是内源性大麻素系统。越来越多的证据提示,内源性大麻素在情绪调节、学习记忆等功能中扮演重要的角色。”张遐介绍说,“我们也许可以特异性地调节人脑内源性大麻素系统的不同方面来帮助人。例如,寻找新的治疗Alzheimer症等神经精神疾病的途径,或者帮助设计新的教育教学技术,促进学生的学习、成长和发展。”
相关论文已于近日发表于《细胞》杂志,陕师大博士生韩静等3名来自中、加、法等国的研究生为共同第一作者。

Acute Cannabinoids Impair Working Memory through Astroglial CB1 Receptor Modulation of Hippocampal LTD
Jing Han, Philip Kesner, Mathilde Metna-Laurent, Tingting Duan, Lin Xu, Francois Georges, Muriel Koehl, Djoher Nora Abrous, Juan Mendizabal-Zubiaga, Pedro Grandes, Qingsong Liu, Guang Bai, Wei Wang, Lize Xiong, Wei Ren, Giovanni Marsicano, Xia Zhang
Impairment of working memory is one of the most important deleterious effects of marijuana intoxication in humans, but its underlying mechanisms are presently unknown. Here, we demonstrate that the impairment of spatial working memory (SWM) and in vivo long-term depression (LTD) of synaptic strength at hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses, induced by an acute exposure of exogenous cannabinoids, is fully abolished in conditional mutant mice lacking type-1 cannabinoid receptors (CB1R) in brain astroglial cells but is conserved in mice lacking CB1R in glutamatergic or GABAergic neurons. Blockade of neuronal glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) and of synaptic trafficking of glutamate α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-isoxazole propionic acid receptors (AMPAR) also abolishes cannabinoid effects on SWM and LTD induction and expression. We conclude that the impairment of working memory by marijuana and cannabinoids is due to the activation of astroglial CB1R and is associated with astroglia-dependent hippocampal LTD in vivo.








