摘要:在真核生物中,RNA前体选择性剪接产生多态性的基因产物,剪接体能够识别特定的剪接位点。本文报道了酵母SRC1 mRNA前体的选择性剪接是由保守性泛素样蛋白Hub1介导,缺少Hub1的剪接体或Hub1-HIND结合错误都会导致前体5’剪接位点识别故障。
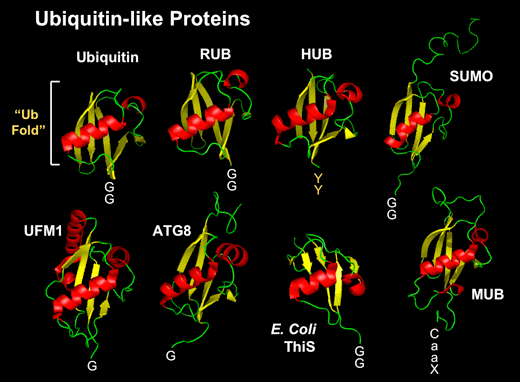
泛素样蛋白三维结构
Alternative splicing of pre-messenger RNAs diversifies gene products in eukaryotes and is guided by factors that enable spliceosomes to recognize particular splice sites. Here we report that alternative splicing of Saccharomyces cerevisiae SRC1 pre-mRNA is promoted by the conserved ubiquitin-like protein Hub1. Structural and biochemical data show that Hub1 binds non-covalently to a conserved element termed HIND, which is present in the spliceosomal protein Snu66 in yeast and mammals, and Prp38 in plants. Hub1 binding mildly alters spliceosomal protein interactions and barely affects general splicing in S. cerevisiae . However, spliceosomes that lack Hub1, or are defective in Hub1–HIND interaction, cannot use certain non-canonical 5′ splice sites and are defective in alternative SRC1 splicing. Hub1 confers alternative splicing not only when bound to HIND, but also when experimentally fused to Snu66, Prp38, or even the core splicing factor Prp8. Our study indicates a novel mechanism for splice site utilization that is guided by non-covalent modification of the spliceosome by an unconventional ubiquitin-like modifier.
全文链接:https://www.nature.com/nature/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nature10143.html?WT.ec_id=NATURE-20110526







