专题:Cell专题
路易斯安那州大学医学院神经科学系,福罗里达州中心大学生物医学中心Wrigh State大学医学院的科学家最近在脑卒中治疗研究方面取得新的进展,相关成果文章公布在Cell杂志上,并且被列为当期的亮点文章。
文章通讯作者是来自,路易斯安那州大学医学院神经科学系的陆有明(Youming Lu)教授,早年毕业于中国药科大学,主要从事脑卒中和阿尔茨海默病的信号分子通路课题研究。
在神经突触外,谷氨酸的主要亚型受体是N-甲基-D-天(门)冬氨酸(NMDA)受体,NMDA与多种细胞内引发不可逆的神经元死亡的分解代谢活动有关。
在本研究中,陆有明教授组的科学家研究分析了小鼠大脑皮层中因脑缺血而诱发的神经元死亡蛋白激酶1(death-associated protein kinase1)与NMDA受体NR2B蛋白复合物的作用过程。
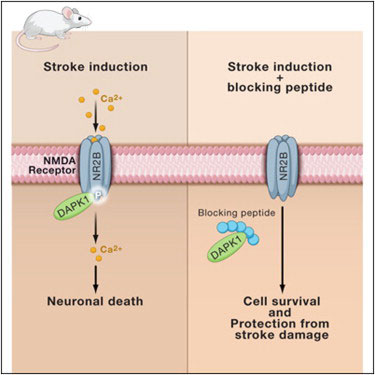
死亡相关蛋白激酶DAPK1可直接与NMDA受体NR2B蛋白氨基端尾巴结合。接下来激活DAPK1磷酸化的NR2B亚单位ser-1303,依次激活NR1/NR2B受体通道的传导效率。如果用遗传学技术将DAPK1基因缺失掉,将导致NR1/NR2B通路失活,导致大脑神经元细胞失去局部缺氧环境的保护伞。
DAPK1在生理和功能上与NMDA受体NR2B亚单位作用,它的功效的发挥与脑卒中有着密切的关联,因此,可能成为治疗脑卒中的一个适当途径。 脑卒中(Stroke)是脑中风学名,是一种突然起病的脑血液循环障碍性疾病。
推荐原始出处:
Cell, Volume 140, Issue 2, 222-234, 22 January 2010 | 10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.055
DAPK1 Interaction with NMDA Receptor NR2B Subunits Mediates Brain Damage in Stroke
Weihong Tu, Xin Xu, Lisheng Peng, Xiaofen Zhong, Wenfeng Zhang, Mangala M. Soundarapandian, Cherine Balel, Manqi Wang, Nali Jia, Wen Zhang, Frank Lew, Sic Lung Chan, Yanfang Chen, Youming Lu
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors constitute a major subtype of glutamate receptors at extrasynaptic sites that link multiple intracellular catabolic processes responsible for irreversible neuronal death. Here, we report that cerebral ischemia recruits death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1) into the NMDA receptor NR2B protein complex in the cortex of adult mice. DAPK1 directly binds with the NMDA receptor NR2B C-terminal tail consisting of amino acid 1292-1304 (NR2BCT). A constitutively active DAPK1 phosphorylates NR2B subunit at Ser-1303 and in turn enhances the NR1/NR2B receptor channel conductance. Genetic deletion of DAPK1 or administration of NR2BCT that uncouples an activated DAPK1 from an NMDA receptor NR2B subunit in vivo in mice blocks injurious Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor channels at extrasynaptic sites and protects neurons against cerebral ischemic insults. Thus, DAPK1 physically and functionally interacts with the NMDA receptor NR2B subunit at extrasynaptic sites and this interaction acts as a central mediator for stroke damage.







