
2014 年,药品评价与研究中心 (CDER) 批准了具有里程碑意义的 41 款新型治疗药物,其中包括 11 款生物制剂(表 1)。去年新药批准数量与 2013 年的 27 个相比增加逾 50%,与五年期平均数量的 31.6 个相比高出 30%。
| Drug (brand name) | Sponsor | Properties | Indications | Review types |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT3, serotonin type 3; A, accelerated approval; ABSSSI, acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; B, breakthrough designation; B-ALL, B-cell acute lymphocytic leukaemia; CDER, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CYP3A, cytochrome P450 3A4; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; FLT3, receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3; GLP1, glucagon-like peptide 1; HCV, hepatitis C virus; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; IL-6, interleukin-6; IPF, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; MOA, mode of action; NK1, substance P; NS, non-structural protein; NSCLC, non-small-cell lung cancer; O, orphan designation; P, priority review; PD1, programmed cell death protein 1; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; PI3Kб, phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase; ROS1, proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS; S, standard review; SGLT2, sodium–glucose cotransporter 2; SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. | ||||
| Dapagliflozin (Farxiga) | AstraZeneca | SGLT2 inhibitor | Type 2 diabetes | S |
| Tasimelteon (Hetlioz) | Vanda | Melatonin-receptor agonist | Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder | P, O |
| Elosulfase alfa (Vimizim) | BioMarin | Hydrolytic lysosomal glycosaminoglycan-specific enzyme | Mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA | P, O |
| Droxidopa (Northera) | Lundbeck | Synthetic amino-acid precursor of noradrenaline; MOA unknown | Light-headedness in patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension | P, O, A |
| Metreleptin (Myalept) | Amylin | Leptin analogue | Leptin deficiency in patients with congenital or acquired generalized lipodystrophy | P, O |
| Florbetaben-F18(Neuraceq) | Piramal Imaging | Radioactive diagnostic agent | Imaging of the brain to estimate density of neuritic amyloid-β plaques | S |
| Miltefosine (Impavido) | Knight | MOA unknown | Leishmaniasis | P, O |
| Apremilast (Otezla) | Celgene | Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor | Psoriatic arthritis and plaque psoriasis | S |
| Albiglutide (Tanzeum) | GlaxoSmithKline | GLP1-receptor agonist | Type 2 diabetes | S |
| Ramucirumab (Cyramza) | Eli Lilly | VEGFR2 antagonist | Gastric cancer | P, O |
| Siltuximab (Sylvant) | Janssen Biotech | IL-6-specific antibody | Multicentric Castleman's disease | P, O |
| Ceritinib (Zykadia) | Novartis | Kinase inhibitor against ALK, IGF1R, insulin receptor and ROS1 | ALK-positive metastatic NSCLC | P, O, B, A |
| Vorapaxar (Zontivity) | Merck & Co. | Protease-activated receptor 1 antagonist | Thrombotic cardiovascular events | S |
| Vedolizumab (Entyvio) | Takeda | Integrin-receptor antagonist | Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease | P |
| Dalbavancin (Dalvance) | Durata | Semisynthetic lipoglycopeptide | ABSSSI | P |
| Efinaconazole (Jublia) | Dow | Azole antifungal | Onychomycosis of the toenails | S |
| Tedizolid (Sivextro) | Cubist | Oxazolidinone-class antibacterial | ABSSSI | P |
| Belinostat (Beleodaq) | Spectrum | Histone-deacetylase inhibitor | Peripheral T-cell lymphoma | P, O, A |
| Tavaborole (Kerydin) | Anacor | Oxaborole antifungal | Onychomycosis of the toenails | S |
| Idelalisib (Zydelig) | Gilead Sciences | PI3Kб inhibitor | CLL, B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma and SLL | P, O, B, A |
| Olodaterol (Striverdi Respimat) | Boehringer Ingelheim | Long-acting β2-adrenoceptor agonist | COPD | S |
| Empagliflozin (Jardiance) | Boehringer Ingelheim | SGLT2 inhibitor | Type 2 diabetes | S |
| Oritavancin (Orbactiv) | The Medicines Company | Semi-synthetic lipoglycopeptide | ABSSSI | P |
| Suvorexant (Belsomra) | Merck & Co. | Orexin-receptor antagonist | Insomnia | S |
| Peginterferon beta-1A (Plegridy) | Biogen Idec | Long-acting interferon-β1A | Relapsing multiple sclerosis | S |
| Eliglustat (Cerdelga) | Genzyme | Glucosylceramide-synthase inhibitor | Gaucher's disease | P, O |
| Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) | Merck & Co. | PD1-specific antibody | Metastatic melanoma | P, O, B, A |
| Naloxegol (Movantik) | AstraZeneca | Opioid-receptor antagonist | Opioid-induced constipation | S |
| Dulaglutide (Trulicity) | Eli Lilly | GLP1-receptor agonist | Type 2 diabetes | S |
| Sulfur hexafluoride lipid-type A microspheres (Lumason) | Bracco | Ultrasound contrast agent | Cardiovascular imaging | S |
| Netupitant plus palonosetron (Akynzeo) | Helsinn | An NK1-receptor antagonist plus a 5-HT3-receptor antagonist | Chemotherapy-related nausea | S |
| Ledipasvir plus sofosbuvir (Harvoni) | Gilead Sciences | An NS5A inhibitor plus an HCV nucleotide-analogue NS5B-polymerase inhibitor | Genotype 1 HCV | P, B |
| Pirfenidone (Esbriet) | InterMune | MOA unknown | IPF | P, O, B |
| Nintedanib (Ofev) | Boehringer Ingelheim | Kinase inhibitor against PDGFRs, FGFRs, VEGFRs and FLT3 | IPF | P, O, B |
| Blinatumomab (Blincyto) | Amgen | CD19- and CD3-bispecific antibody | B-ALL | P, O, B, A |
| Finafloxacin (Xtoro) | Alcon | Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial | Acute otitis externa (swimmer's ear) | P |
| Olaparib (Lynparza) | AstraZeneca | PARP inhibitor | Advanced BRCA-mutated ovarian cancer | P, O, A |
| Ombitasvir plus paritaprevir plus dasabuvir plus ritonavir (Viekira Pak) | AbbVie | An NS5A inhibitor plus an NS3A- and NS4A-protease inhibitor plus a non-nucleoside NS5B-palm-polymerase inhibitor plus a CYP3A inhibitor | Chronic HCV genotype 1 infection | P, B |
| Ceftolozane plus tazobactam (Zerbaxa) | Cubist | A cephalosporin antibacterial plus a β-lactamase inhibitor | Complicated intra-abdominal infections and complicated urinary tract infections | P |
| Peramivir (Rapivab) | BioCryst | Neuraminidase inhibitor | Influenza infection | S |
| Nivolumab (Opdivo) | Bristol-Myers Squibb | PD1 inhibitor | Unresectable or metastatic melanoma | P, O, B, A |
表1:2014年CDER批准的生物制剂
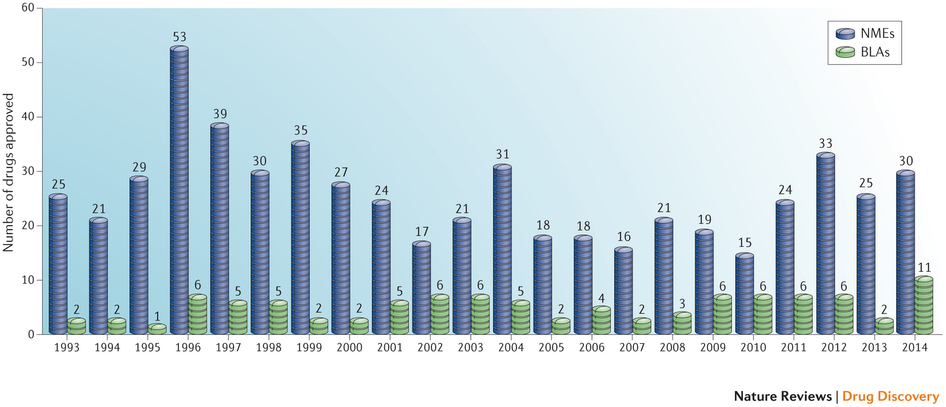
图 1:自 1993 年以来新药批准数量
此图显示了药品评价与研究中心 (CDER) 自 1993 年来批准的新分子实体 (NMEs) 与生物制剂许可申请。生物制剂评价与研究中心 (CBER) 批准的产品未包括在这一药品数量当中。数据来自 Drugs@FDA 及 FDA。
位于美国马萨诸塞州波士顿的塔夫斯药品开发研究中心的研究主任 Milne 称,“作为多产的一年,我给它打一个满分。”他指出,尽管美国 FDA 在 1996 年批准了更多的药物,有 53 个之多,但 1996 年是不同寻常的一年,FDA 在这一年进行了监管改革,需要清理积压的申请,从而也促使批准数量增多。“这使得 2014 年成为药品审批成绩更大的一年,” Milne 如是称。
然而,就创新来讲,Milne 认为 2014 年药品批准刚刚及格。他指出药品批准名单中包含相当数量的同类竞争产品,制药公司在寻求批准作用于已证明的相同靶点及同种适应症的药物。例如,FDA 批准了 4 款 2 型糖尿病的药物,但达格列净与 Empagliflozin 分别属于二类及三类钠葡萄糖协同转动蛋白 2(SGLT2) 抑制剂,而阿必鲁泰与 Dulaglutide 分别属于四类及五类胰高血糖素样肽 1(GLP1) 受体激动剂。“这里存在某些从众心理,”他指出称。
从商业角度看,2014 年批准的药物看起来可能还不如数量虽少但商业潜能大的 2013 年批准药物。波士顿咨询集团 (BCG) 跟踪了少量潜力较大的批准药物,包括生物制剂评价与研究中心 (CBER)(表 2)及补充新药申请(sNDA) 批准的药物,预测 2014 年批准的 53 个值得注意的药物将会产生 480 亿美元的合并峰值销售(图 2)。
相比之下,他们跟踪的 2013 年批准的 36 款产品有望获得 530 亿美元的合并峰值销售。“2014 年是不可思议的一年,” BCG 高级合作伙伴 Schulze 称。但他补充称,2013 年批准药物的峰值销售可能下降,在某种程度上来说是因为 2014 年批准的许多新药正在使市场竞争更加激烈。
| Drug brand name | Sponsor | Properties | Indication |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBER, Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research; Fc, crystallizable fragment. | |||
| Trumenba | Wyeth/Pfizer | Meningococcal group B vaccine | Meningitis B |
| Obizur | Baxter | Recombinant porcine antihaemophilic factor | Acquired haemophilia A |
| Hyqvia | Baxter | Immunoglobulin infusion with recombinant hyaluronidase | Humoral immune defects in adults with primary immunodeficiency |
| Ruconest | Pharming | Recombinant C1-esterase inhibitor | Hereditary angioedema |
| Eloctate | Biogen Idec | Recombinant antihaemophilic factor–Fc fusion protein | Haemophilia A |
| Ragwitek | Merck & Co. | Short ragweed pollen allergen extract | Short ragweed pollen-induced allergic rhinitis |
| Grastek | Merck & Co. | Timothy grass pollen allergen extract | Grass pollen-induced allergic rhinitis |
| Oralair | Stallergenes | Sweet vernal grass, orchard grass, perennial rye, Timothy grass and Kentucky Bluegrass mixed pollen allergen extract | Grass pollen-induced allergic rhinitis |
| Alprolix | Biogen Idec | Recombinant coagulation factor IX–Fc fusion protein | Haemophilia B |
表 2:2014 年 CBER 批准药物
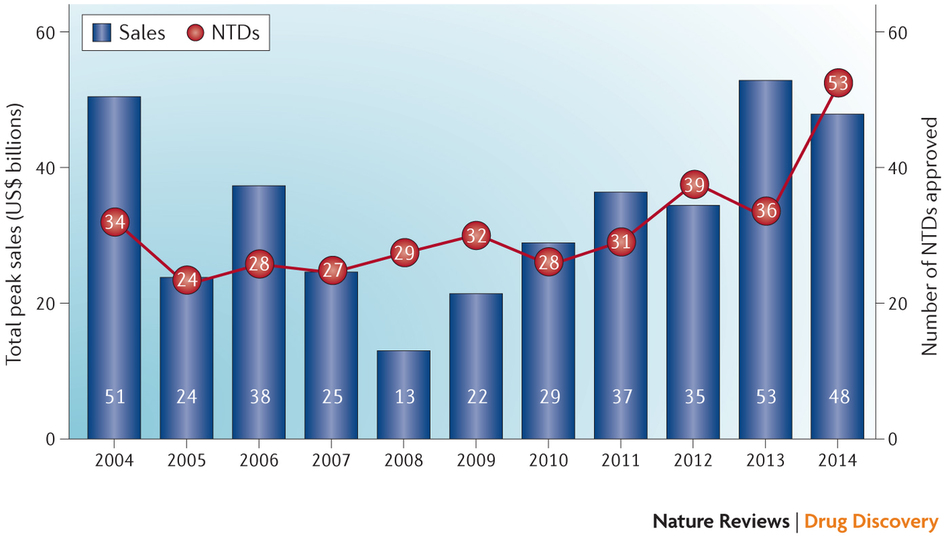
图 2:自 2004 年以来批准药物合并峰值销售
药品合并峰值销售预测由波士顿咨询集团 (BCG) 精心计算。BCG 的分析师考虑了 2014 年批准的 53 款新型治疗药物的峰值销售预测,包括新分子实体 (NMEs) 及药物评价与研究中心 (CDER) 批准的生物制剂许可申请 (BLAs),剔除了批准的医学影像产品,加上了 CDER 及生物制剂评价与研究中心(CBER) 批准的某些非 NME。全面地对 2014 年批准药物的峰值销售数据进行预测。真实的销售数据及更新的预测用于早些年批准的药物。
CDER 批准的药物中有 12 款药物 (29%) 被认为会在五年内成为重磅炸弹级药物,而其中只有 3 款药物 (7%) 有望突破 20 亿美元大关(图 3)。2013 年批准的药物中有 13 款药物 (48%) 在五年内有望达到重磅炸弹级地位,其中有 6 款药物 (22%) 的年销售额有望超过 20 亿美元。
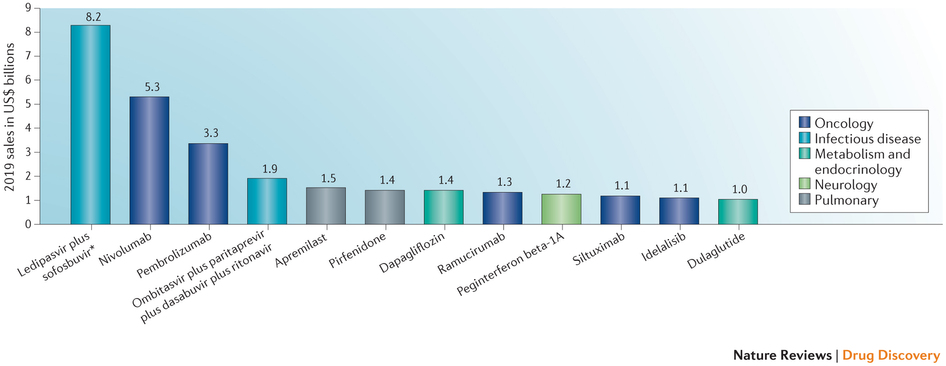
图 3:2014 年批准的有望成为重磅炸弹级的药物
销售预测是 2019 年的平均、年度、全球预测,由汤森路透 Cortellis 数据库编制。“吉利德 Ledipasvir 与 Sofosbuvir 的复方药物到 2017 年有望达到 120 亿美元峰值销售。
2014 年批准的多款潜在重磅炸弹级药物包括这一年最令人兴奋的科学批准。默沙东的 Pembrolizumab 与百时美施贵宝的 Nivolumab 是首批程序性细胞死亡蛋白 1(PD1) 抑制剂类癌症免疫治疗药物,肿瘤专家希望通过将这类药物与其它免疫治疗药物、激酶抑制剂及化疗药物混合搭配,他们可以改变癌症治疗的现状。
与此同时,吉利德科学 Ledipasvir 与 Sofosbuvir 的固定剂量复方药物从竞争激烈的药物开发中脱颖而出,成为首个用于基因型 1 丙型肝炎病毒 (HCV) 感染的全口服治疗药物。明年,在几个令人激动的科学领域还可能看到后期试验项目,包括胆固醇酯转移蛋白 (CETP) 抑制剂、前蛋白转化酶枯草溶菌素 9(PCSK9)抑制剂及溶瘤病毒(表 3)。
| Drug name | Sponsors | Properties | Indication | Event due in 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event data are from BioMedTracker. CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; CETP, cholesteryl ester transfer protein; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; IL-17, interleukin-17; JAK, Janus kinase; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9; PDUFA, Prescription Drug User Fee Act. | ||||
| Secukinumab | Novartis | IL-17-specific antibody | Psoriasis | PDUFA decision in January |
| Palbociclib | Pfizer | CDK inhibitor | Breast cancer | PDUFA decision in April |
| Toujeo | Sanofi | Insulin glargine | Diabetes | PDUFA decision in May |
| Talimogene laherparepvec | Amgen | Oncolytic virus | Melanoma | PDUFA decision in July |
| Evolocumab | Amgen | PCSK9-specific antibody | Hypercholesterolaemia | PDUFA decision by September |
| Lumacaftor plus ivacaftor | Vertex | CFTR corrector and CFTR potentiator | Cystic fibrosis | PDUFA decision in November |
| Alirocumab | Sanofi/Regeneron | PCSK9-specific antibody | Hypercholesterolaemia | PDUFA decision |
| LCZ696 | Novartis | Angiotensin-receptor inhibitor and neutral-endopeptidase inhibitor | Congestive heart failure | PDUFA decision |
| Ryzodeg | Novo Nordisk | Co-formulation of insulin degludec and insulin aspart | Diabetes | Cardiovascular outcomes data, to address 2012 complete response letter |
| Anacetrapib | Merck & Co. | CETP inhibitor | Hypercholesterolaemia | Interim efficacy analysis of Phase III trial |
| Ocrelizumab | Roche | CD20-specific antibody | Multiple sclerosis | Top-line Phase III data |
| Baricitinib | Eli Lilly | JAK1- and JAK2- inhibitor | Rheumatoid arthritis | Top-line Phase III data |
表 3:2015 年视目以待的药物
FDA 在 2014 年首次审评即批准的药物比率为 67%,低于 2013 年的 78%(表 4 列出了 2014 年一些收到完全回应函或被申请者撤回的药物)。
| Drug | Sponsor | Properties | Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
*Indicates agents that were withdrawn. ADP, adenosine diphosphate; NS, non-structural protein. | |||
| Cangrelor | The Medicines Company | P2Y12 platelet ADP-receptor inhibitor | Acute coronary syndrome and following coronary artery bypass graft |
| Serelaxin | Novartis | Agonist for relaxin receptors 1–4 | Acute decompensated heart failure |
| Macrilen | Æterna Zentaris | Ghrelin-receptor agonist | Short stature or growth-hormone deficiency |
| Daclatasvir* | Bristol-Myers Squibb | NS5A inhibitor | Hepatitis C virus |
| Daclatasvir plus asunaprevir* | Bristol-Myers Squibb | An NS5A inhibitor plus an NS3 protease inhibitor | Hepatitis C virus |
表 4:2014 年被 FDA 拒绝或撤回的药物
批准药物治疗领域出现分化
去年,FDA 批准了 9(22%) 款肿瘤药物(图 4),2013 年与 2012 年分别为 9(33%) 款和 13 (33%) 款。“问题是你要看到相对值或绝对值,” Schulze 称。“我认为其它领域的创新正在爆发,肿瘤药物的相对份额正在削弱,”他补充称。
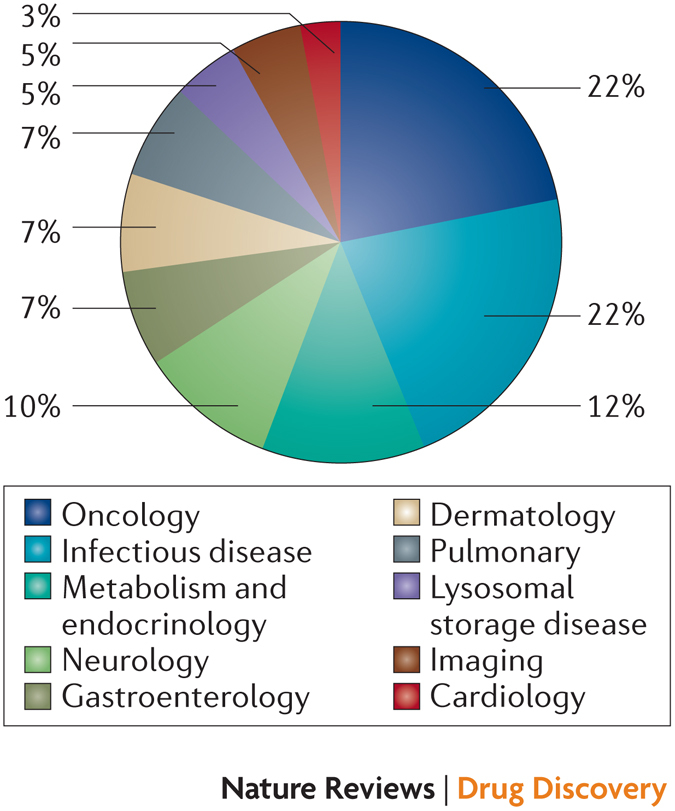
图 4:批准治疗领域
感染疾病也获批了 9 款药物 (22%),高于 2013 年的 3 个(11%)。除了 HCV 及 HIV 新药,感染疾病增添了 4 款抗生素,它们均是在合格感染产品(QIDP) 计划下得到批准的。这些 QIDP 抗生素中有 3 款产品用于治疗皮肤感染。然而,此次抗生素获批的小幅增长可能主要由于几年前引入的急性细菌性皮肤及皮肤组织感染 (ABSSSI) 试验指南的改变,而非抗生素药物开发基本问题的变化。
目前为止,2014 年是批准孤儿药最多的一年,批准的药物中有 17 款药物 (41%) 获得了孤儿药资格。相比之下,FDA 在 2013 年批准了 9 个 (33%) 孤儿新分子实体(NMEs),2012 年是 13 个(33%),2011 年是 11 个(37%)。2014 年批准的每一款肿瘤药物均用于孤儿适应症。
FDA 在 2014 年还以突破性治疗药物资格批准了 9 款 (22%) 药物。据 BCG 分析师称,这些药物包含了 2014 年批准新药 50% 的商业潜能。批准的 12 款有望达到重磅炸弹级资格的药物中有 6 款药物是突破性治疗药物,包括 4 款有最高销售预测的药物。没有迹象表明 FDA 在授予突破性治疗药物资格上要减少数量,对制药业来说这是一个令人鼓舞的数据。
CDER 批准新药名单中包括 11 款生物制剂 (27%),高于 2013 年的 2 个(7%) 及 2009-2012 年间每年的 6 个(15–29%)。
FDA 通过加速批准通道批准了 8 款药物 (20%)。“这很棒,” Milne 称,因为《FDA 安全与创新法案》的目标之一是通过鼓励使用代理标志物而更多地利用加速批准通道。但他补充称,获得加速批准的药物中有 7 款药物被批准用于癌症,所以这一审评通道的应用在其它治疗领域仍有许多可以改进的地方。
拓展阅读:







